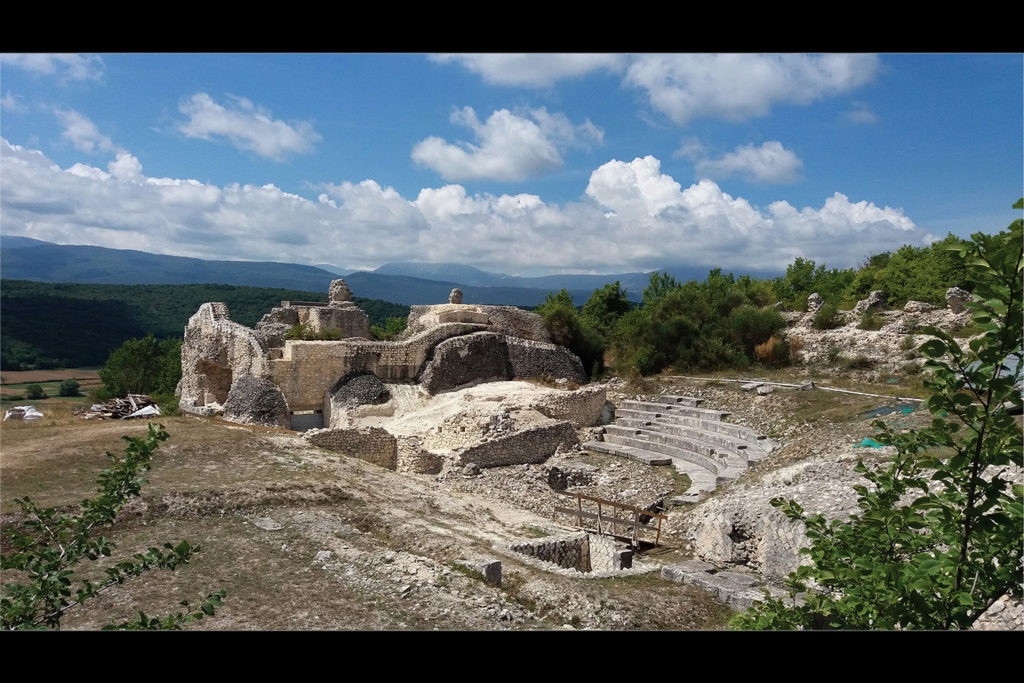
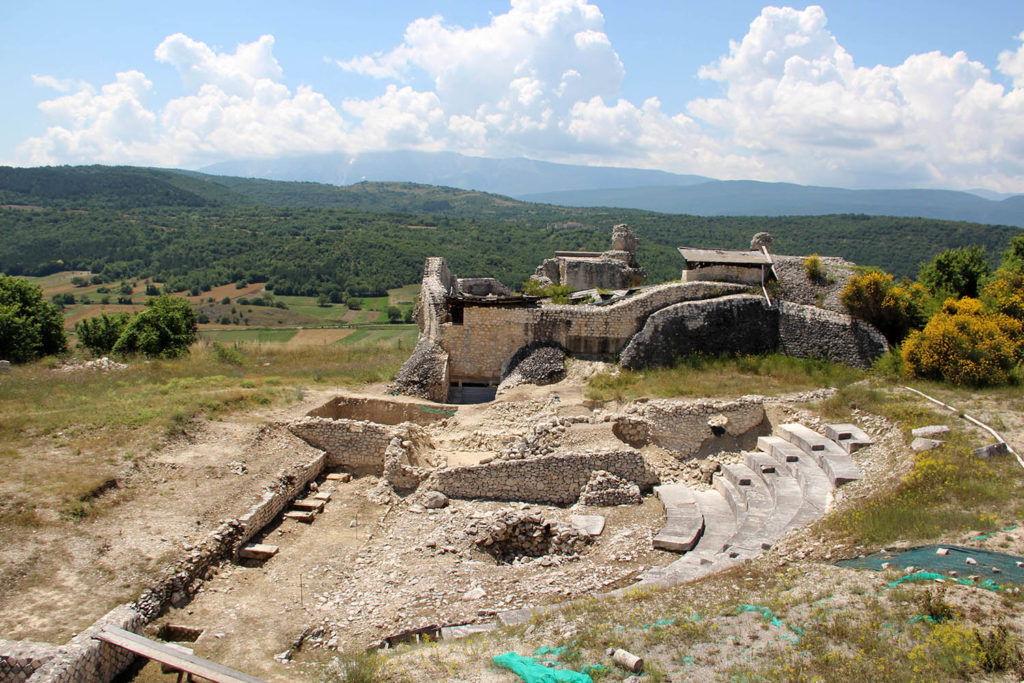
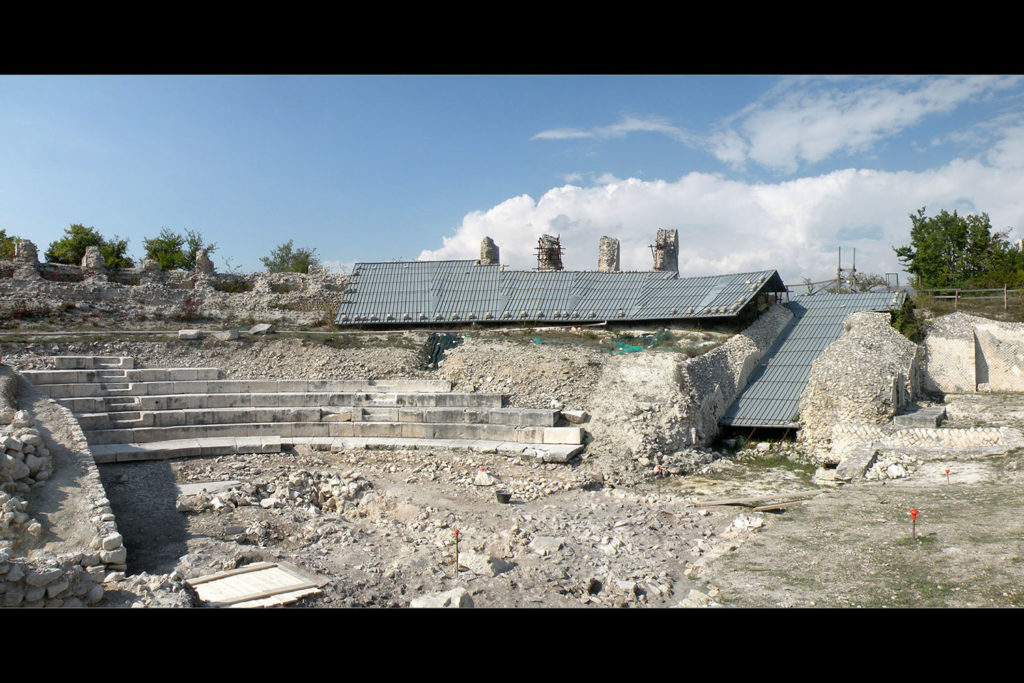
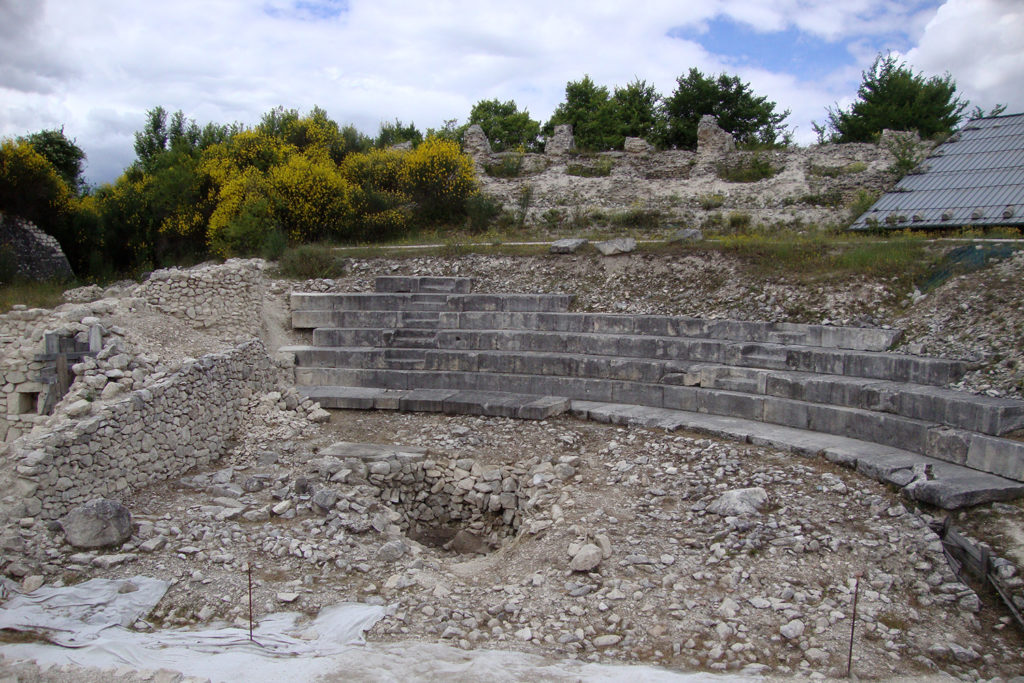
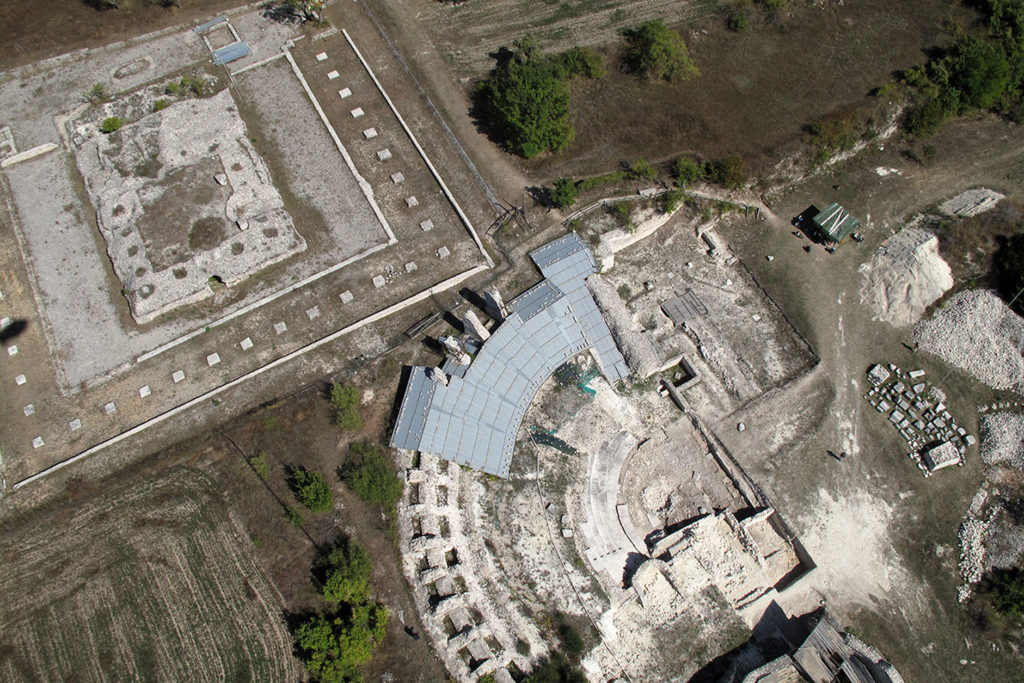
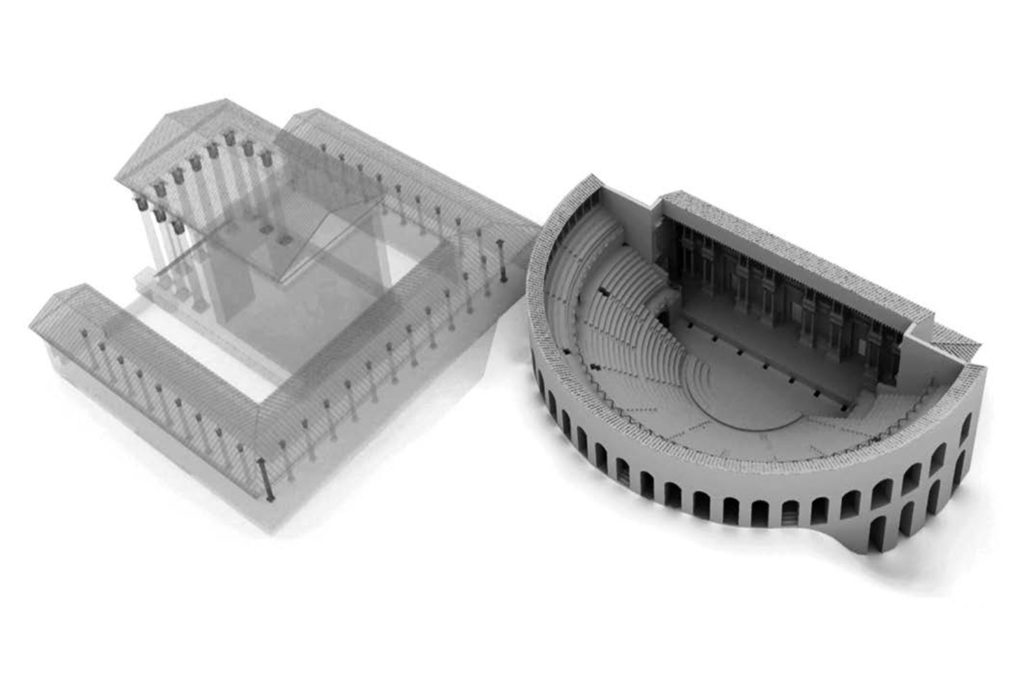
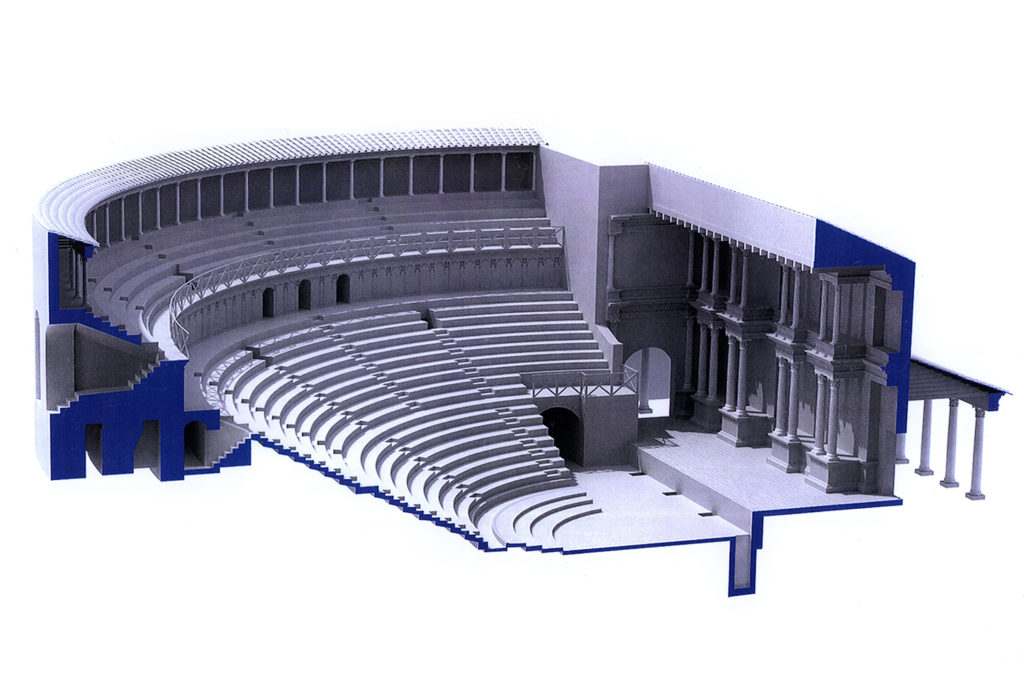
The Theatre
The theatre was built almost entirely appoggando seats for spectators at the hillside, only the southern ector was supported by radial walls. With this system, the theatre was also the foundation wall of the terrace on which the temple was, and consequently the northern entrance connecting the two levels with a ramp flight of steps. In the course of its use, the theatre was hit by several earthquakes of great intensity and not only that caused restoration, the earthquake of the fifth century of disastrous proportions for the city, said beginning the activity of dispossession that has left only a few steps in the lower part of the auditorium, the walls in the upper part supporting the places intended for the less well off (the “pigeon”).
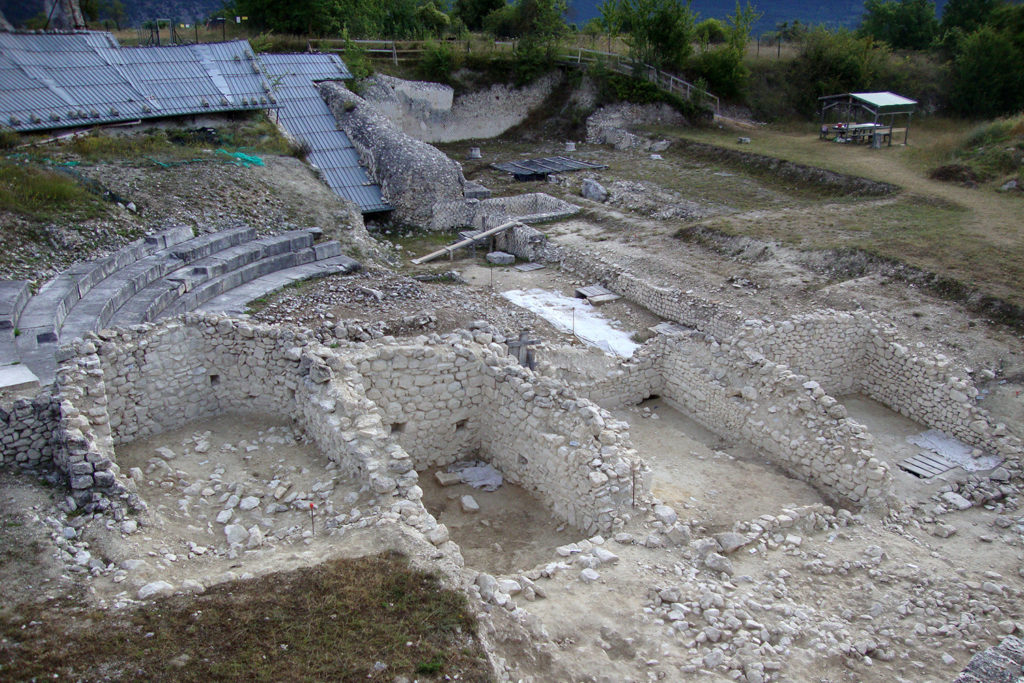
The area used for the representation are still currently visible part of the stage and the foundations of the fifth stage. The complex system by which rose and fell the curtain retain the wells within which they moved the wooden poles which was tied the tarp and the room which was controlled by the winch connected to them, as in the Roman theatre, the curtain rose to cover the scene changes and fell during the performance. Poor are the remains of the porch for walks during the interval in the shows.
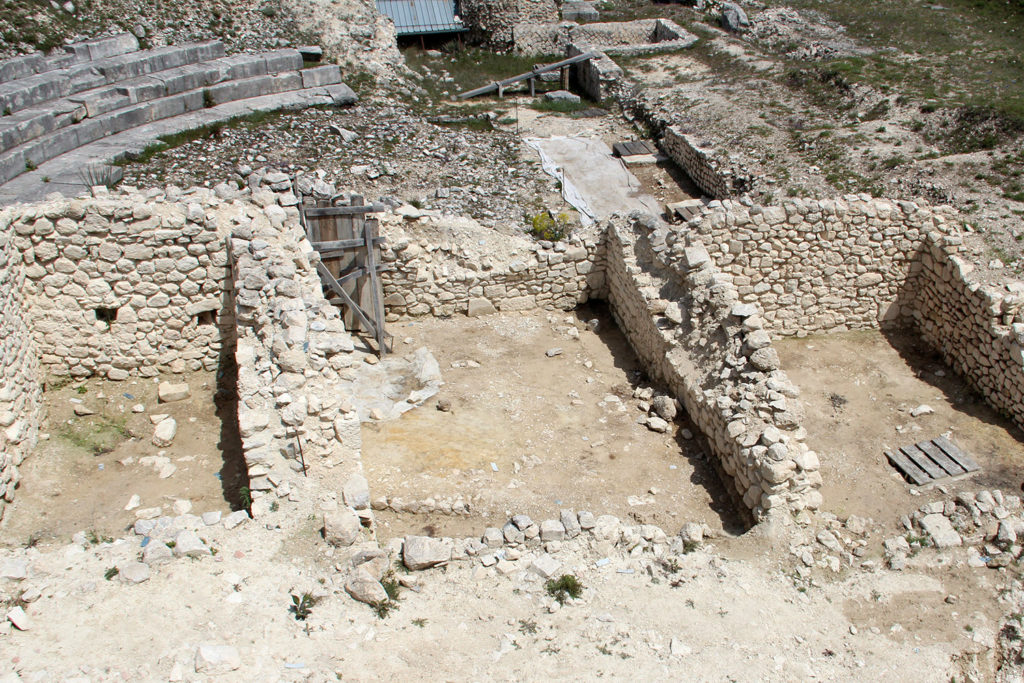
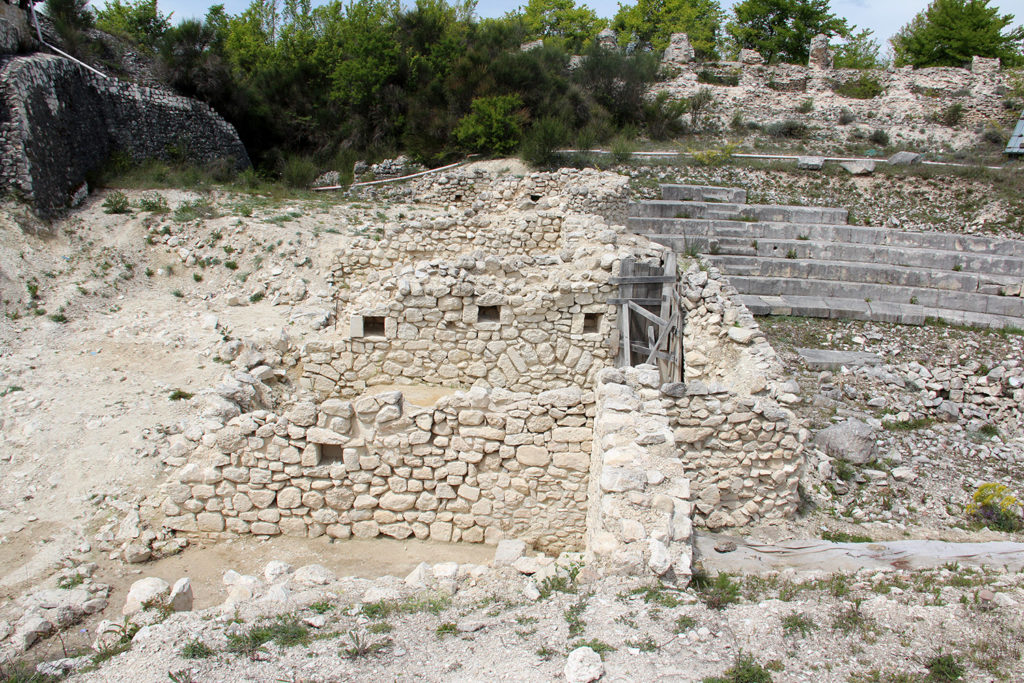
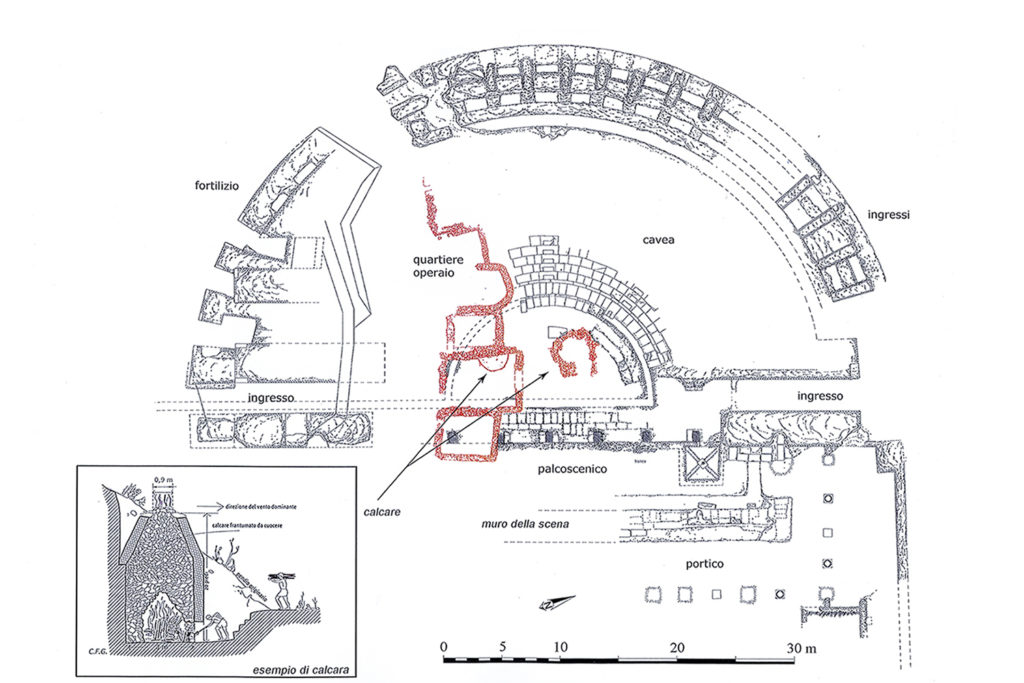
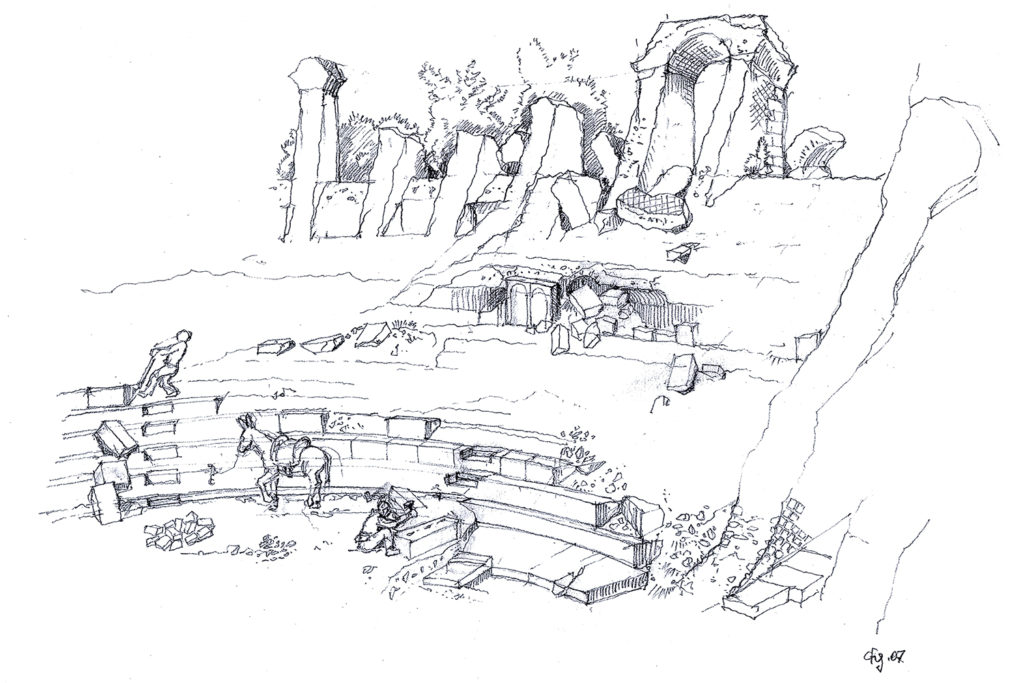
After the earthquake of the fifth century the theatre became a quarry for building materials, such as the temple, at first it was used for the installation of two lime kilns (limestone). Subsequently, in the southern part, after the complete removal of the bleachers, it was built a working-class neighborhood for the rework of materials for some of the various reconstructions of the nearby church of St. Paul. In particular, the ceramic materials found in an
environment lead to tie the plant of the yard to the phase of rebuilding following the earthquake in the first half of 1349. Feature environments is the presence of niches in the walls (a kind of small closets).
In the period of battlements the southern sector of the theatre was used for the installation of a fortified lookout with the control function of the valley to the south of the plateau.